Kicking off with Using Heatmaps for UX, this topic delves into the world of data visualization to improve user experience. Heatmaps are powerful tools that provide valuable insights into user behavior, guiding designers to make informed decisions for optimal UX design.
Introduction to Heatmaps
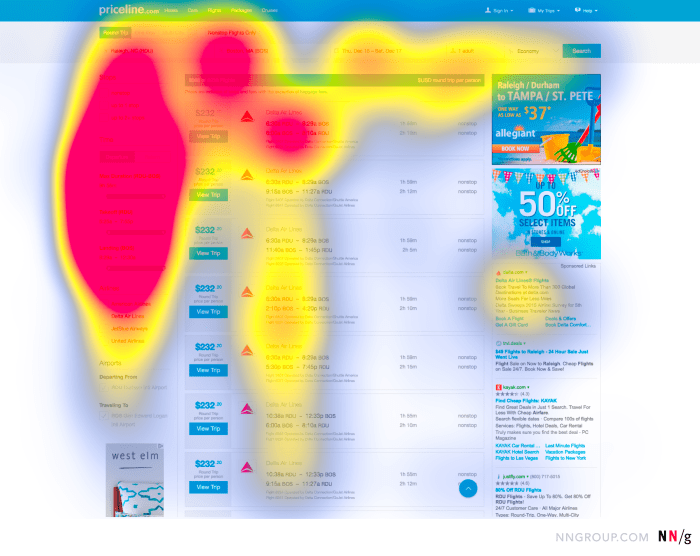
Heatmaps are visual tools used in UX design to analyze and understand user behavior on websites or apps. By displaying data in a graphical format, heatmaps help designers identify patterns, trends, and areas of interest on a webpage.
Types of Heatmaps
There are several types of heatmaps commonly used in UX design:
- Click Heatmaps: These show where users are clicking the most on a webpage, indicating areas of high engagement.
- Scroll Heatmaps: Scroll heatmaps display how far down a page users are scrolling, helping designers determine the most valuable content placement.
- Move Heatmaps: These track mouse movement on a webpage, revealing how users navigate and interact with the interface.
- Attention Heatmaps: Attention heatmaps indicate areas where users are spending the most time, providing insights into what captures their interest.
Benefits of Using Heatmaps
Using heatmaps for UX analysis offers a variety of advantages that can help designers make informed decisions and improve the overall user experience. By visually representing user behavior on a website or app, heatmaps provide valuable insights into how people interact with the interface.
Identifying User Engagement Levels
- Heatmaps can show which areas of a webpage or app receive the most attention from users, helping designers prioritize important content and calls to action.
- By analyzing click heatmaps, designers can understand where users are clicking most frequently, allowing them to optimize the placement of buttons or links for better usability.
Tracking Scrolling Behavior
- Scroll heatmaps reveal how far users scroll down a page before losing interest, enabling designers to adjust content placement and length accordingly.
- Understanding where users drop off can help improve the overall user experience and increase engagement.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
- Heatmaps can highlight common user behaviors, such as repeated clicks on non-clickable elements or areas of high hover activity, allowing designers to make data-driven design decisions.
- By recognizing patterns and trends, designers can create more intuitive interfaces that cater to user preferences and expectations.
Types of Heatmaps
In the world of UX analysis, different types of heatmaps play a crucial role in understanding user behavior and optimizing websites or applications. Let’s dive into the various types of heatmaps and their specific purposes.
Click Heatmaps
Click heatmaps visually represent where users are clicking on a web page. By showing hotspots of user clicks, this type of heatmap helps identify which elements are attracting the most attention. Click heatmaps are valuable for understanding user engagement and can highlight areas that may need improvement, such as call-to-action buttons or navigation links.
- Example: Use a click heatmap to analyze the effectiveness of your website’s menu navigation. Identify which menu items receive the most clicks and rearrange the menu structure accordingly for a better user experience.
Scroll Heatmaps
Scroll heatmaps track how far down the page users are scrolling before leaving. This type of heatmap provides insights into user engagement and helps identify where users lose interest or abandon the page. Scroll heatmaps are useful for optimizing content placement and ensuring key information is visible without excessive scrolling.
- Example: Utilize a scroll heatmap to determine the optimal placement of important content on your landing page. Identify the fold line where users tend to stop scrolling and adjust content placement to improve visibility and engagement.
Move Heatmaps, Using Heatmaps for UX
Move heatmaps track the movement of users’ cursors on a webpage, highlighting areas of interest or confusion. By visualizing cursor movement, move heatmaps help identify user behavior patterns and interactions with different page elements. This type of heatmap can reveal which elements users find engaging or distracting.
- Example: Employ a move heatmap to analyze user interaction with a complex form on your website. Identify areas where users hover the cursor the most or encounter difficulties, and optimize the form layout for a smoother user experience.
Interpreting Heatmap Data: Using Heatmaps For UX
When it comes to interpreting heatmap data, it’s all about understanding how users are interacting with your website or app. By analyzing the visual representation of user behavior, you can gain valuable insights that can help improve the overall user experience.
Common Metrics and Indicators
- Clicks: The number of times a specific element is clicked on can indicate user interest or confusion.
- Scroll Depth: Shows how far down the page users are scrolling, highlighting popular content areas.
- Hover Behavior: Reveals where users are lingering or showing interest without clicking.
- Attention Mapping: Indicates which areas are getting the most visual attention from users.
Best Practices for Analysis
- Look for Patterns: Identify recurring trends or hotspots that can guide changes to layout or content.
- Compare Heatmaps: Analyze different heatmap types (click, scroll, move) to get a comprehensive view of user interactions.
- Combine with Other Analytics: Use heatmap data in conjunction with other analytics tools for a complete understanding of user behavior.
- Test and Iterate: Implement changes based on heatmap insights, test them, and continue refining for optimal UX improvements.
Implementing Heatmaps in UX Design
Implementing heatmaps in UX design can greatly enhance the understanding of user behavior and interaction with a website or app. By following a few key steps and utilizing the right tools, designers can effectively integrate heatmaps into the design process to optimize user experience.
Integrating Heatmaps into the Design Process
- Choose the right heatmap tool: Select a reliable heatmap tool that meets the specific needs of the project, whether it’s click heatmaps, scroll heatmaps, or move heatmaps.
- Implement the heatmap tracking code: Integrate the heatmap tracking code into the website or app to start collecting data on user interactions.
- Analyze heatmap data: Review and interpret the heatmap data to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement in the user experience.
- Make design decisions based on heatmap insights: Use the insights gained from heatmaps to make informed design decisions that prioritize user needs and preferences.
Tools and Software for Creating and Analyzing Heatmaps
- Hotjar: A popular tool for creating heatmaps, recording user sessions, and gathering feedback through surveys and polls.
- Crazy Egg: Known for its user-friendly interface and detailed heatmaps that provide insights into user behavior.
- Mouseflow: Offers heatmaps, session replays, and conversion funnels to track user interactions and improve UX design.
Tips for Effectively Using Heatmaps
- Combine heatmap data with other UX research methods: Use heatmaps in conjunction with user testing, surveys, and analytics to gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior.
- Focus on key areas of interest: Prioritize analyzing heatmaps for critical pages or elements that have a significant impact on user engagement and conversions.
- Regularly review and update heatmaps: Continuously monitor and update heatmaps to reflect changes in user behavior and design improvements over time.